Oracle などで Create sequence するように Counter 専用のModel を作成して、
increment("xxxx")するようにしたほうがよいのか。 Writes are expensive!
- Datastore is transactional: writes require disk access
- Disk access means disk seeks
- Rule of thumb: 10ms for a disk seek
- Simple math:
- 1s / 10ms = 100 seeks/sec maximum
- Depends on:
- The size and shape of your data
- Doing work in batches (batch puts and gets)
Reads are cheap!
- Reads do not need to be transactional, just consistent
- Data is read from disk once, then it's easily cached
- All subsequent reads come straight from memory
- Rule of thumb: 250usec for 1MB of data from memory
- Simple math:
- 1s / 250usec = 4GB/sec maximum
- For a 1MB entity, that's 4000 fetches/sec
Tools for storing data: Entities
- Fundamental storage type in App Engine
- Set of property name/value pairs
- Most properties indexed and efficient to query
- Other large properties not indexed (Blobs, Text)
- Think of it as an object store, not relational
- Kinds are like classes
- Entities are like object instances
- Relationship between Entities using Keys
- Reference properties
- One to many, many to many
Tools for storing data: Entity groups 2
Hierarchical
- Each Entity may have a parent
- A "root" node defines an Entity group
- Hierarchy of child Entities can go many levels deep
- Watch out! Serialized writes for all children of the root
Datastore scales wide
- Each Entity group has serialized writes
- No limit to the number of Entity groups to use in parallel
- Think of it as many independent hierarchies of data
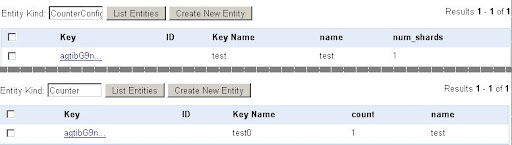
class CounterConfig(db.Model):
name = db.StringProperty(required=True)
num_shards = db.IntegerProperty(required=True,default=1)
class Counter(db.Model):
name = db.StringProperty(required=True)
count = db.IntegerProperty(required=True,default=0)
def get_count(name):
total = 0
for counter in Counter.gql('WHERE name = :1', name):
total += counter.count
return total
def increment(name):
config = CounterConfig.get_or_insert(name,name=name)
def txn():
index = random.randint(0, config.num_shards - 1)
shard_name = name + str(index)
counter = Counter.get_by_key_name(shard_name)
if counter is None:
counter = Counter(key_name=shard_name, name=name)
counter.count += 1
counter.put()
db.run_in_transaction(txn)
increment("test")
print get_count("test")
def get_count(name):
total = memcache.get(name)
if total is None:
total = 0
for counter in Counter.gql('WHERE name = :1', name):
total += counter.count
memcache.add(name, str(total), 60)
return total
def increment(name):
config = CounterConfig.get_or_insert(name,name=name)
def txn():
index = random.randint(0, config.num_shards - 1)
shard_name = name + str(index)
counter = Counter.get_by_key_name(shard_name)
if counter is None:
counter = Counter(key_name=shard_name,name=name)
counter.count += 1
counter.put()
db.run_in_transaction(txn)
memcache.incr(name)
http://sites.google.com/site/io/building-scalable-web-applications-with-google-app-engine